Documentation >
Reference Manual for GigaFlow >
System >
GigaFlow ClusterLocated at System > GigaFlow Cluster.
A single GigaFlow server can be configured to search for IP addresses across many remote GigaFlow servers directly from Viavi's Apex system. This feature is useful for large organisations that may have many GigaFlow servers monitoring different networks within the organisation, e.g. in different regions. The central administrator may want a view across the entire network, e.g. to determine if a particular suspect IP address has been recorded by routers on different networks.
In this example, assume that you are the main administrator and you want visibility on several remote GigaFlow servers.
The set-up is:
- GigaFlow Server #0: this is the server at HQ, used by the main administrator. We call this the Pitcher.
- GigaFlow Server #1: this is remote GigaFlow server #1. We call this Receiver 1.
- GigaFlow Server #2: this is remote GigaFlow server #2. We call this Receiver 2.
- GigaFlow Server #3: this is remote GigaFlow server #3. We call this Receiver 3.
Figure: Defining a GigaFlow cluster
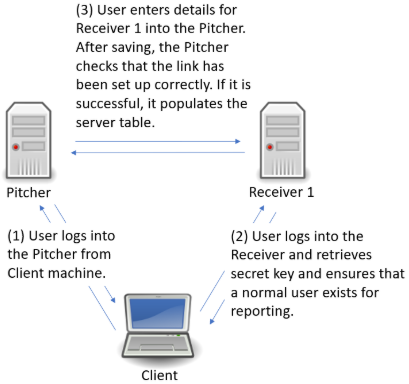
Log in to GigaFlow Server #0, the Pitcher, and navigate to System > GigaFlow Cluster.
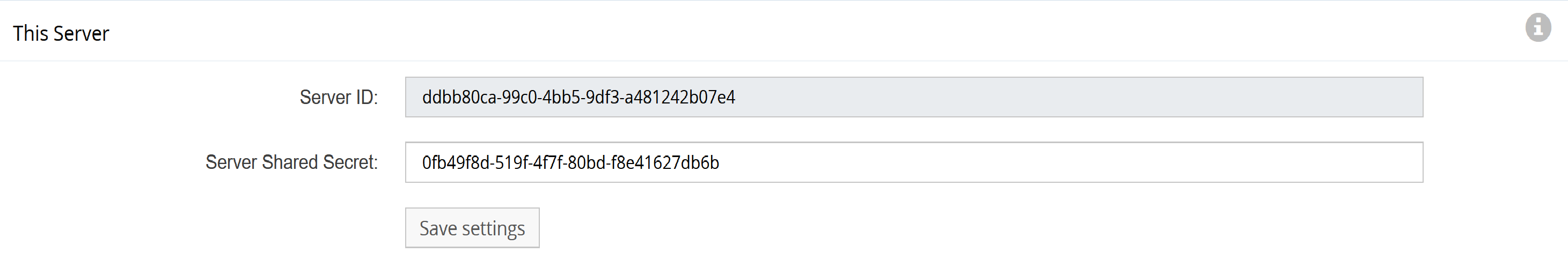
In the This Server panel, you will see a pre-generated unique secret. Leave this as is.
In another browser tab or window, log into Receiver 1 (GigaFlow Server #1). Copy the unique secret from Receiver 1's This Server panel. You do not need to do anything with the New Cluster Server panel on the receivers.
Figure: This Server panel
Switch back to the Pitcher (GigaFlow Server #0). In the New Cluster Server panel:
- Enter a name that you will see during a search across servers, i.e. Receiver 1.
- Enter the description that you will see when hovering-over the server name during a search across servers, e.g. "EMEA GigaFlow server (Receiver 1)".
- Enter the full IP address, including port number, used to connect to Receiver 1, i.e. in the format "http(s)://172.1.1.0:22".
- Enter the IP address of the Pitcher system as seen by Receiver 1. This IP address is used by the Pitcher to generate a secure hashed key for communication. The Receiver reverses this hash using, among other things, the IP address of the Pitcher. An intermediate firewall (NAT) could create problems if the Pitcher does not create the hashed key using the IP address seen by the Receiver.
- Enter the UserID used when making superuser calls to Receiver 1, e.g. Admin. This is used during this set-up process.
- Enter the UserID that will be used when making report requests, e.g. reportuser; this is used by all clients when collecting data from the Receiver. This user must exist on Receiver 1. If it does not exist, switch to Receiver 1 and create a new normal user on Receiver 1, i.e. reportuser.
- Paste Receiver 1's secret, i.e. the key copied from Receiver 1's This Server panel.
- Click Save
 to add the Receiver 1.
to add the Receiver 1. - The Pitcher will connect to Receiver 1 using the Admin user to verify that everything is correct and to populate the table at bottom of the System page. Receiver 1 will appear in the main table.
Figure: New Cluster Server panel

Repeat this process for Receiver 2 and Receiver 3.
The cluster server feature is flexible; a receiver in one cluster can be a pitcher for another.
The Cluster Access panel shows cluster access status. The table lists:
- ID: Cluster ID.
- Added: Time and date.
- By: User.
- Net State: network state, up or down.
- Admin State: admin status, i.e. details on its operation.
- Reporter State: success or fail.
- Settings: JSON object.
- Actions: delete.
Following the search link from Apex, you will be brought to a new tab and the log in screen for the Pitcher machine. After logging in, you will be brought to the GigaFlow Cluster report page. This displays a list of hits for this IP address across the cluster; in this example, the IP address might be found on devices monitored by all three receivers. Clicking on a receiver name brings up the forensics report summary for that IP address from that receiver in the table at the bottom of the summary page. Alongside each receiver on the results page is a link out to that particular server.
Figure: Conducting a GigaFlow Cluster search
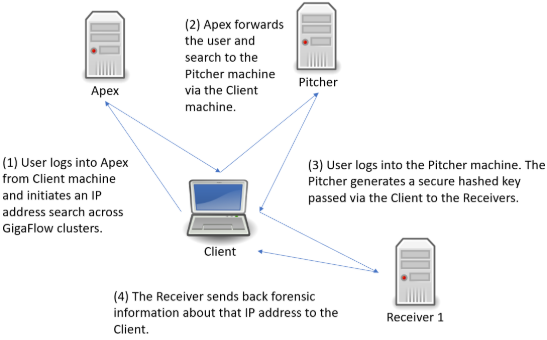
See also Reports > Cluster Search.
Communication between all clients in a Gigaflow cluster is IP to IP, i.e. unicast. The traffic is routed over https, using TLS based on certificates.



